Using the API (v1)
This page should help you use and understand the API and its functionality.
Make sure to check the automatic documentation under //localhost:<port>/ or //localhost:<port>/docs. There you can also find more information on the request schemas and responses.
General Information
The CAMELS API works by sending HTTP requests to its web server.
To use any request other than the home path of the web server you need to authenticate your request using the API key (see Creating API Keys).
If you are using a regular browser and want to use the API manually it is best to navigate to <host>:<port>. You can then select the request you want to perform and click on Try it out and then Execute.
You will be need to authenticate yourself to send any API requests. Simply enter the API key in the password section. The username can be anything or empty. This will look something like this
Once authorized in the browser you will stay authenticated when using further requests until you close the browser.
Most Useful Commands
Below are descriptions for the most useful commands.
Attention
In the following all paths are given als relative paths from //localhost:<port>/.
Get Protocol Parameters
Use these requests to find out which protocols exists and what variables each protocol has.
GET: Get available Protocols
You can get all protocol names that are currently available in CAMELS by going to
/api/v1/protocols
You can also use Python to perform the http request. This could look something like:
import requests
api_key = "123abc" # Enter the actual API key you got from CAMELS here
# Create the headers with the Bearer token
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}"
}
port = 5000 # Change this to the port you are acutally using
result = requests.get(f"http://localhost:{port}/api/v1/protocols", headers=headers)
The API will return a JSON string of the form:
{"Protocols":["ProtocolXYZ","DefaultProtocol","..."]}
GET: Protocol Variables
Get the changeable variables of a protocol:
/api/v1/protocols/variables/{protocol_name}
Executing Protocols
Every time you execute a protocol via the API a unique identifier (UUID) is generated and a URL is returned where you can check on the current status of that protocol.
The UUID is saved together with the current run status to the SQLite database file CAMELS_API.db under protocol_run_status.
The status can either be currently in queue, currently running or the file path to the data if the protocol finished.
If you go to the URL returned by the request, for example:
{
"check protocol status here": "/api/v1/protocols/results/ae593c12-8938-4e24-b05b-77c169f10f76"
}
and the protocol is finished you will be able to get the path to the measurement file under status:
{
"uuid":"ae593c12-8938-4e24-b05b-77c169f10f76",
"status":"C:\\Users\\User\\Documents\\NOMAD_CAMELS_data\\default_user\\default_sample\\data_2024-08-08T14-26-13.848567+02-00.nxs"
}
There are two ways you can directly execute a protocol you defined in CAMELS via the API:
If you want to queue protocols see here for more information.
GET: Run Protocols
Note
Make sure to add the required bearer token authentication in the header of the request. See for example Python code here
GET /api/v1/actions/run/protocols/{protocol_name}
This will directly execute the Protocol with the name protocol_name.
This is equivalent to pressing the run-button on a protocol.
In response to the request, you will receive the UUID, which allows you to track the current state of the protocol. See Executing Protocls or Protocol Results for more information on protocol status.
POST: Run Protocols with Variables
Note
POST requests can NOT be performed using a regular browser. You can use the /docs section of the FastAPI to manually use the API or do it programmatically.
POST /api/v1/actions/run/protocols/{protocol_name}
body: {
"variables": {
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
}
}
You can modify variables that are defined in the protocol and then execute the protocol with the newly defined variables.
To do this you must change the "key1" to match the variable name and the "value1" to the desired value.
For a protocol like this
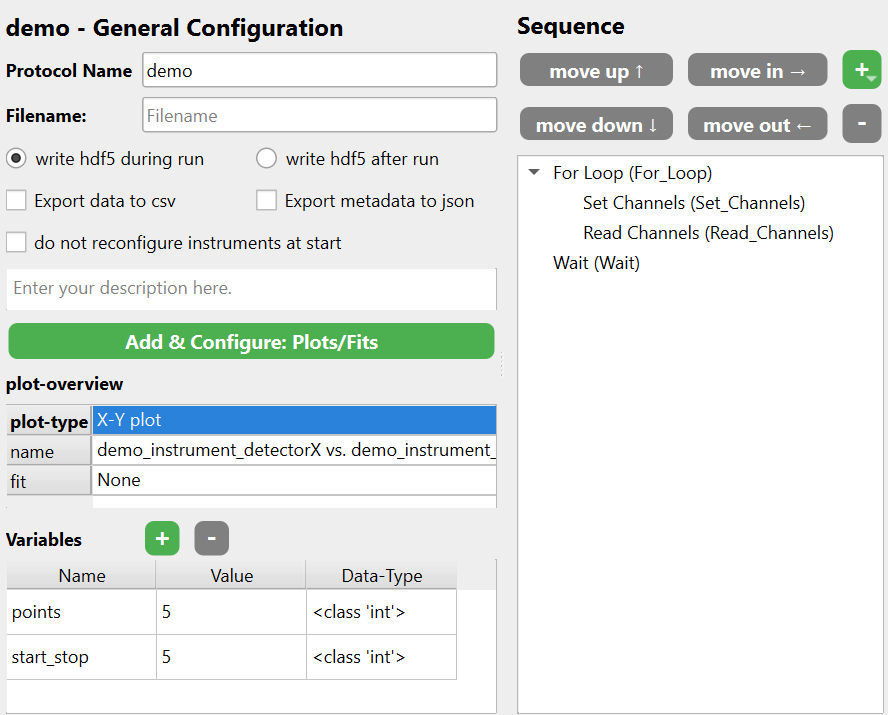
You could use a body like
body: {
"variables": {
"points": 21,
"start_stop": 7
}
}
Using Python this could look like this
import requests
api_key = "123abc" # Enter the actual API key you got from CAMELS here
protocol_name = 'demo' # Change this to the name of the protocol you are using
body = {'variables': {
'points': 21,
'start_stop':7
}
}
# Create the headers with the Bearer token
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}"
}
port = 5000 # Change this to the port you are acutally using
result = requests.post(
f"http://127.0.0.1:{port}/api/v1/actions/run/protocols/{protocol_name}",
headers=headers,
json=body
)
print(result.json())
In response to the request, you will receive the UUID, which allows you to track the current state of the protocol execution.
{'check protocol status here': '/api/v1/protocols/results/6949df94-9170-4d00-aee1-62580e9e75f5'}
Protocol Queue
There is protocol queue that allows you to create a list of protocols that are executed after each other.
There are two ways you can add a protocol to the queue either “as-is” so the same as pushing the green “queue” button or you can again modify the variables.
GET: Add Protocol to Queue
/api/v1/actions/queue/protocols/{protocol_name}
In response to the request, you will receive the UUID, which allows you to track the current state of the protocol.
The status can either be currently in queue, currently running or the file path to the data.
POST: Add Protocol to Queue and Change Variables
/api/v1/actions/run/protocols/{protocol_name}
body: {
"variables": {
"points": 21,
"start_stop": 7
}
}
In response to the request, you will receive the UUID, which allows you to track the current state of the protocol.
The status can either be currently in queue, currently running or the file path to the data.
POST: Change Variables of Protocol in Queue
If you already added a protocol to the queue but want to change its variables afterwards you can use this request.
/api/v1/actions/queue/variables/protocols/{protocol_name}_{index}
body: {
"variables": {
"points": 21,
"start_stop": 7
}
}
Again give the name of the protocol (for example demo) and the index of where it is in the queue. The index starts with 0 for the first (top-most) protocol.
Note
You can also use -1 to access the last element.
In Python this can look like this
protocol_name = 'demo'
index = 0
body = {'variables': {'start_stop': 10, 'points': 31}}
api_key = "123abc" # Enter the actual API key you got from CAMELS here
# Create the headers with the Bearer token
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}"
}
result = requests.post(
f"http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/v1/actions/queue/variables/protocols/{protocol_name}_{index}",
headers=headers,
json=body,
)
GET: Protocol Ready
When checking the ready button in the queue the protocol will be execuited if it is the first in the row. This allows you to chain several protocols and run them consecutively.
To check a protocol with the API use
/api/v1/actions/queue/ready/protocols/{protocol_name}_{index}
Again give the name of the protocol (for example demo) and the index of where it is in the queue. The index starts with 0 for the first (top-most) protocol.
GET: Get Current Protocol Queue
To get the current protocol queue list use
/api/v1/queue
GET: Remove Protocol from Queue
To remove a protocol from the current queue use
/api/v1/actions/queue/remove/protocols/{protocol_name}_{index}
Again give the name of the protocol (for example demo) and the index of where it is in the queue. The index starts with 0 for the first (top-most) protocol.
Protocol Results
Every protocol run will generate data. Either into a single file or individual HDF5 files for each measurement. You can check the current status of the measurement using the command found below.
To be able to retrieve the results of a protocol run via the API you can either get the file path for the data file created or get the actual file.
Warning
Retrieving the actual data file can crash for large files. Only do this if you are sure that the file is small enough to be handled by your RAM and browser.
Protocol Results File Path
To get the file path to where the data is stored use
/api/v1/protocols/results/{protocol_uuid}
If the protocol is still in the queue or is not finished yet it will return currently in queue or currently running respectively.
Protocol Results File
To get the actual file use
/api/v1/protocols/results/{protocol_uuid}/file
If the protocol is still in the queue or is not finished yet it will display currently in queue or currently running respectively.
Measurement Metadata
You can get and modify the measurements metadata like the user performing the measurement, the sample used or a session name to better describe what you are doing.
GET: Samples
You can get all the available samples using
/api/v1/samples
GET: Set Sample
You can set the current sample by using
/api/v1/actions/set/samples/{sample_name}
GET: Users
You can get all the available users using
/api/v1/users
GET: Set User
You can set the current user by using
/api/v1/actions/set/users/{user_name}
GET: Session Description
You can get the current session description by using
/api/v1/session
GET: Set Session Description
You can set the current session description by using
/api/v1/actions/set/session/{session_name}


